Netmiko Service Common Parameters
These are the Netmiko Common Parameters for all Netmiko Services.
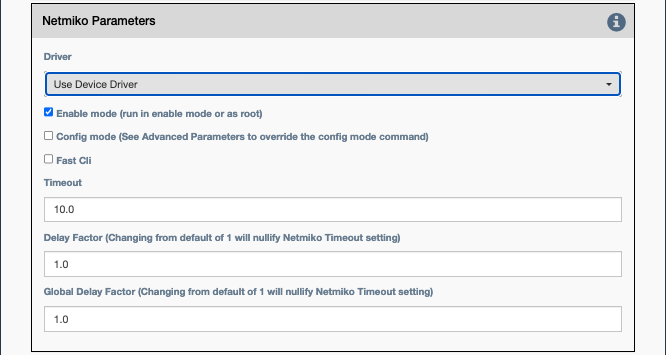
Common Netmiko Parameters
Driver: This selects which Netmiko driver to use when connecting to the device. IfUse Device Driveris checked, the service will use the Netmiko driver from the inventory that is associated with the device. Otherwise, override and select a particular driver.
Note
In some cases it is useful to override the driver. One particular example is that Napalm Ping is not supported for IOS-XR devices, but the user can override the driver to IOS and use the Napalm Ping functionality in that driver (ping works the same everywhere; it is not dependent on driver functionality).
Enable mode: If checked, Netmiko should enter enable/privileged mode on the device before running the command or applying the configuration block. For the Linux driver, this means root/sudo.Config mode: If checked, Netmiko should enter config mode.Fast CLI: If checked, Netmiko will disable internal wait states and delays in order to execute the service as fast as possible.Timeout: Netmiko internal timeout in seconds to wait for a connection or response before declaring failure.Delay factor: Netmiko multiplier used to increase internal delays (defaults to 1). Delay factor is used in the send_command Netmiko method. See here for more explanation.Global delay factor: Netmiko multiplier used to increase internal delays (defaults to 1). Global delay factor affects delays beyond Netmiko send_command. Increase this for devices that have trouble buffering and responding quickly. Practical max value is 5.
Connection Parameters
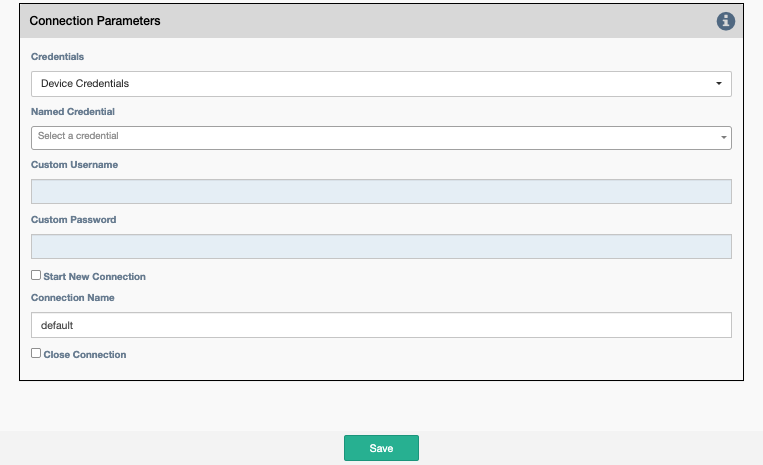
Credentials: Select between:Device Credentials: The application will select the most appropriate credential object for each device. If there are multiple credentials available, theType of CredentialandPriorityproperties become a tiebreaker.Named Credentials: Allows users to reference a specific credential for all targets. Selecting this option requires additional selections below.Custom Credentials: Allows users to store a credential against this service. Selecting this option requires additional selections below.
Advice
Named Credentials selections will persist through duplicating a service, unlike Custom Credentials.
For details on creating a Named Credential take a look at this page.
Named Credential: Select from a list of user created credential objects.Custom Username: User provided username, stored against this service.-
Custom Password: User provided password, stored against this service. -
Start New Connection: before the service runs, the current cached connection is discarded and a new one is started. -
Connection Name: If changed to something other thandefault, the connection will be cached as a separate connection to that same device. This allows for multiple simultaneous "named" connections to a single device. -
Close Connection: Once the service is done running, the current connection will be closed.
Jump on connect Parameters
Jump on connect is designed to allow a second connection after connecting to the original device.
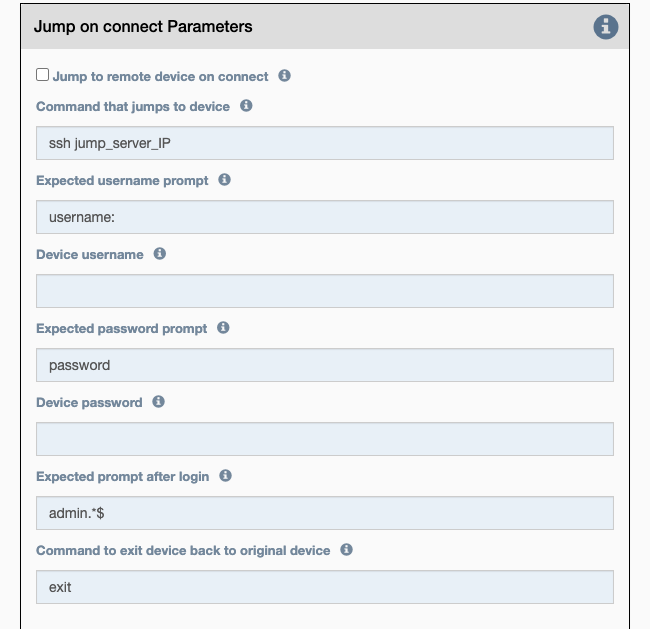
Jump to remote device on connect: If checked, the config items below will be used to connect to the secondary device.Command that jumps to device: Command to initiate secondary connection.Expected username prompt: Prompt expected when connecting secondary connection.Device username: The username to send when the expected username prompt is detected.Expected password prompt: Prompt expected when connecting secondary connection.Device password: The password to send when the expected password prompt is detected.Expected prompt after login: Prompt expected after successfully negotiating a connection.Command to exit device back to original device: Command required to exit the secondary connection.
Note
A number of the above colored text fields support variable substitution