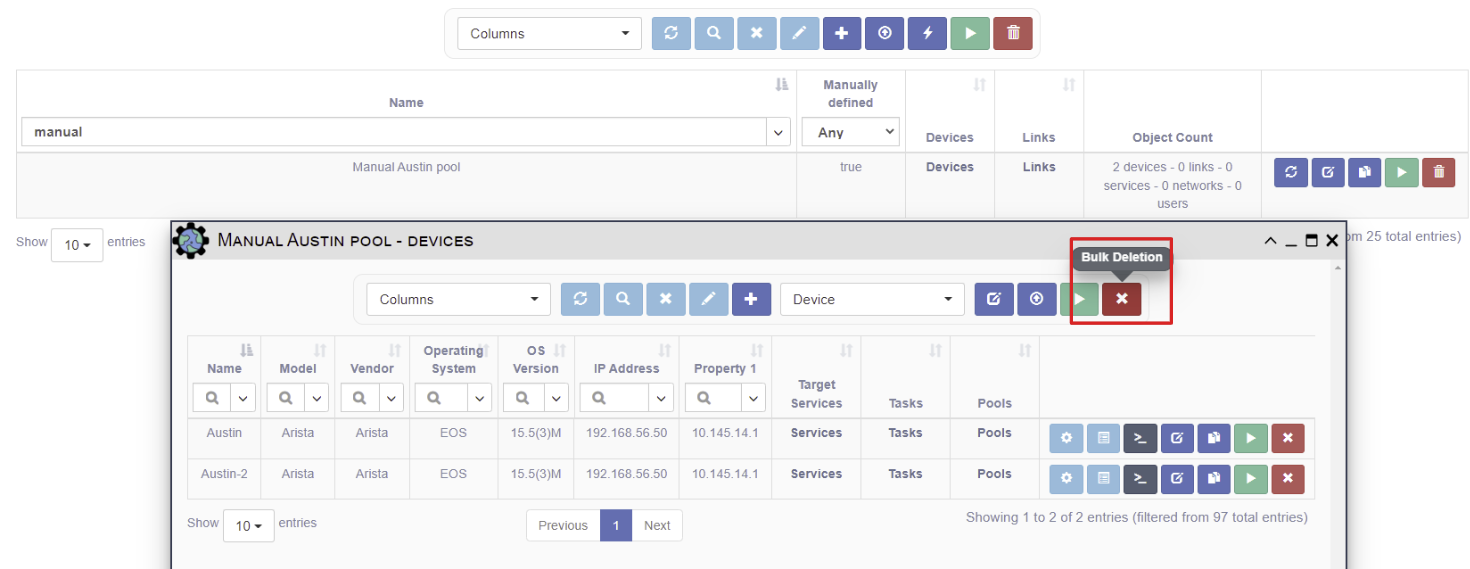
Pools
Overview
A Pool is a collection of device and/or link objects. When defining a Pool, a combination of selection properties are specified that define a match based on inclusion, equality, or regular expression; this match determines which devices and links are included in the Pool. If the properties of an object matches the pool properties, that object is automatically included in the pool. Alternatively, pools can be edited to manually select objects instead of using criteria based on properties.
Pools of devices and links can also be used to define the objects displayed in
the Geographic View and in the Network Builder Visualization panels.
Pools are used in several parts of the application:
-
Targets of a Service or Workflow: Devices can be added to a pool, which is then selected as the execution target for a Service or Workflow automation to run on.
- Pools can also be specified as the execution targets of a Scheduled Task. If a pool is also specified as the target within the service or workflow, the Scheduled Task's pool overrides which devices the automation executes against.
-
Visualization Scope:
- Geographical Visualization: pool selection is used to filter which objects are presented on the map. The pool list only shows pools with devices and links.
- Network Builder: displays existing Network objects (from
Inventory -> Networks) on the graph. TheAdd to Networkbutton allows pools of devices and links (as well as individual devices and links) to be added to the currently displayed Network.
-
Advanced Search / Relationship Based Filtering: Pools can be targets for the union, intersection, or empty match in order to filter a table in the application.
Pool Management
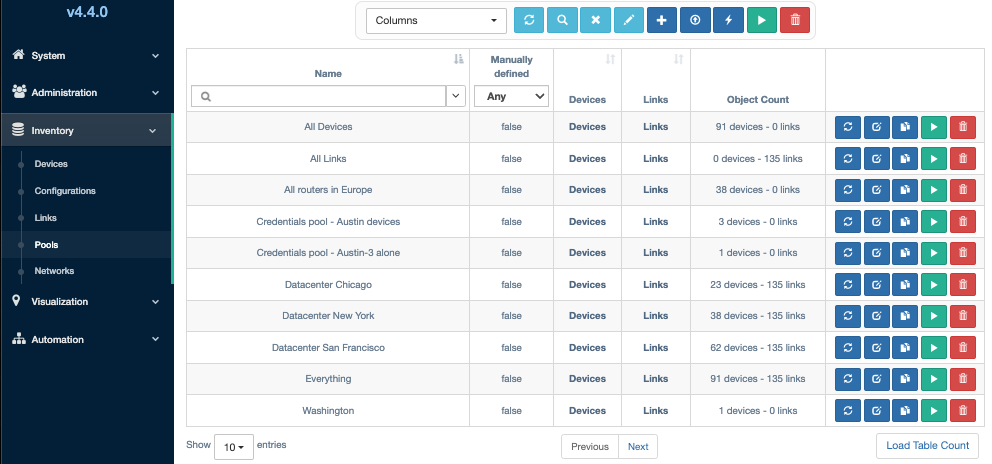
The Inventory -> Pools menu supports the following operations on each pool
listed in the Pools table:
-
Update: Recalculate membership in the pool based on the current pool properties and object properties to determine which objects are now included in the pool.
-
Edit: Modify the properties for matching this pool.
-
Duplicate: Copy this pool's properties to a new pool and make some slight modification for different criteria.
-
Run Service: Run a service or workflow against this pool's devices.
-
Delete: Delete this pool.
The following operations are supported from the menu bar above the table. Note that bulk operations apply to all currently displayed pools based on filtering or advanced search criteria:
-
Refresh: Refresh the table.
-
Advanced Search: Apply an advanced filter against the table to select which pools are displayed.
-
Clear Search: Clear all filtering that has been applied to the table.
-
Copy Selection to the Clipboard: Copy the list of Pools to the clipboard as a comma-separated list.
-
New: Create a new Pool of objects.
-
Export: Export the list of Pools as a .csv file that is downloaded to the user's browser.
-
Update All Pools: Recalculate pool membership for all Pools.
-
Run Service on All Pools in the Table: Run a Service or Workflow using all the pools in the table as the combined set of execution targets.
-
Bulk Deletion: Delete all pools currently displayed in the table.
Managing Pool Access
User maintained Access Control is available for this object. This allows the Owners to select desired access.
Check out this page for more details on modifying Access Control.
Device Pool Creation Example
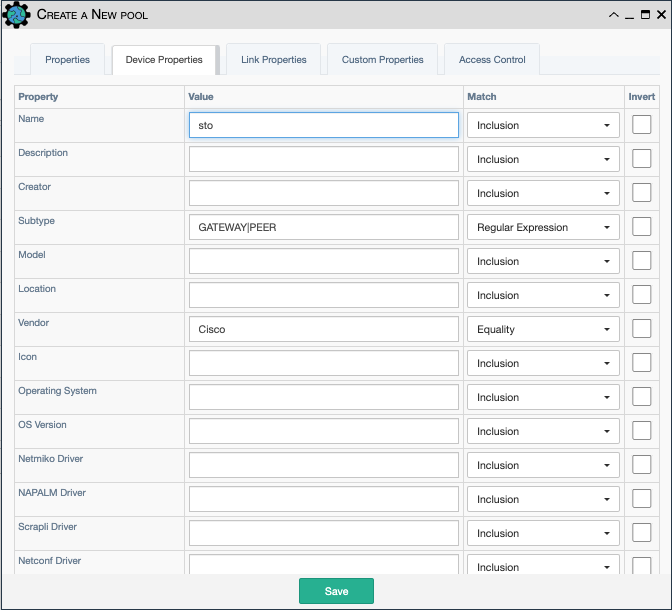
This pool enforces the intersection of the following conditions:
- name:
sto- Match is Inclusion; all devices whose name includessto.BostonandHoustonboth match. - subtype:
GATEWAY|PEER- Match is Regular Expression; all devices having subtypeGATEWAYorPEERwill be selected. - vendor:
Cisco- Match is Equality; all devices whose vendor isCiscowill be selected.
In summary, all Cisco devices with subtype GATEWAY or PEER whose name includes
sto will match these conditions and be included as members of the pool.
Note
-
All empty properties are ignored unless the
Emptymatch option is selected. This option matches objects where the property is empty, e.g. not defined. -
The
Invertcheckbox reverses the logic for that parameter. So ifCiscois specified in the vendor field,Invertwill cause all devices to match whose vendor is NOTCisco. -
Along with all properties of a device, you can use the device's collected
ConfigurationandOperational Dataas a constraint for the pool.
Links Pool Creation Example
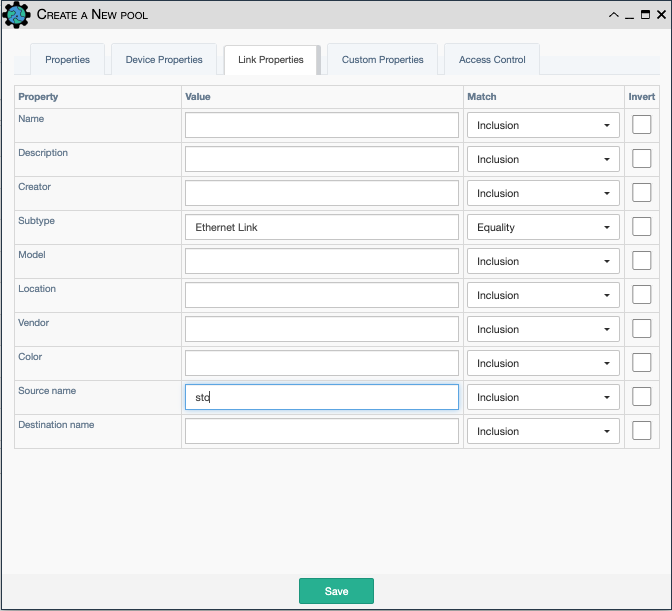
This pool enforces the intersection of the following conditions:
- subtype:
Ethernet link: Match is Equality; all Ethernet links will be selected. - source name:
sto- Match is Inclusion; all links whose source name includes the stringstoare matched, e.g.BostonandHouston.
In summary, all Ethernet Link(s) starting with source devices whose name includes
sto will be members of the pool.
Default Pools
Three pools are created by default in eNMS:
All objects: A pool that matches all Devices and Links.Devices only: A pool that matches all Devices, no Links.Links only: A pool that matches all Links, no Devices.
Pools Based on Configuration
Pools can be created by searching the configuration data collected from all of the devices, rather than just the Inventory parameters for each device. Configuration collection must be first configured, and then allowed to run at least once before the data exists for pool matching.
Filter the View with a Pool
Pools can be used as filters for Devices and Links on the geographical
view: Visualization -> Geographical View. The first alphabetical pool in the list
will be displayed on the map by default, so make sure to create a smaller pool to
display as the default if your inventory is large. Use the pool selector at the top
to change the displayed devices and links.
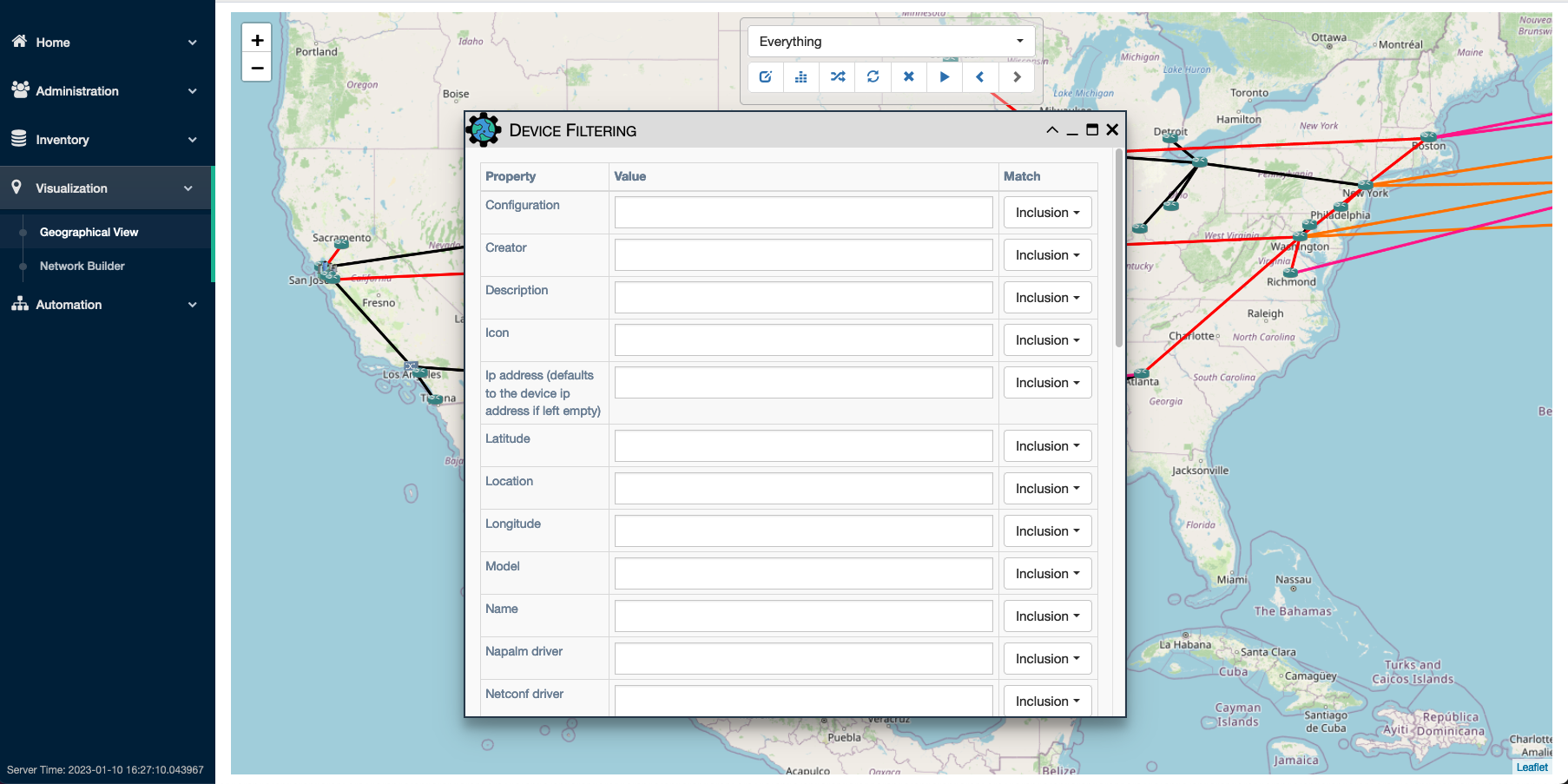
Use a Pool as target of a Service or a Workflow
In Service Edit Panel -> Step 3, select Device(s) and/or Pool(s) as target(s).
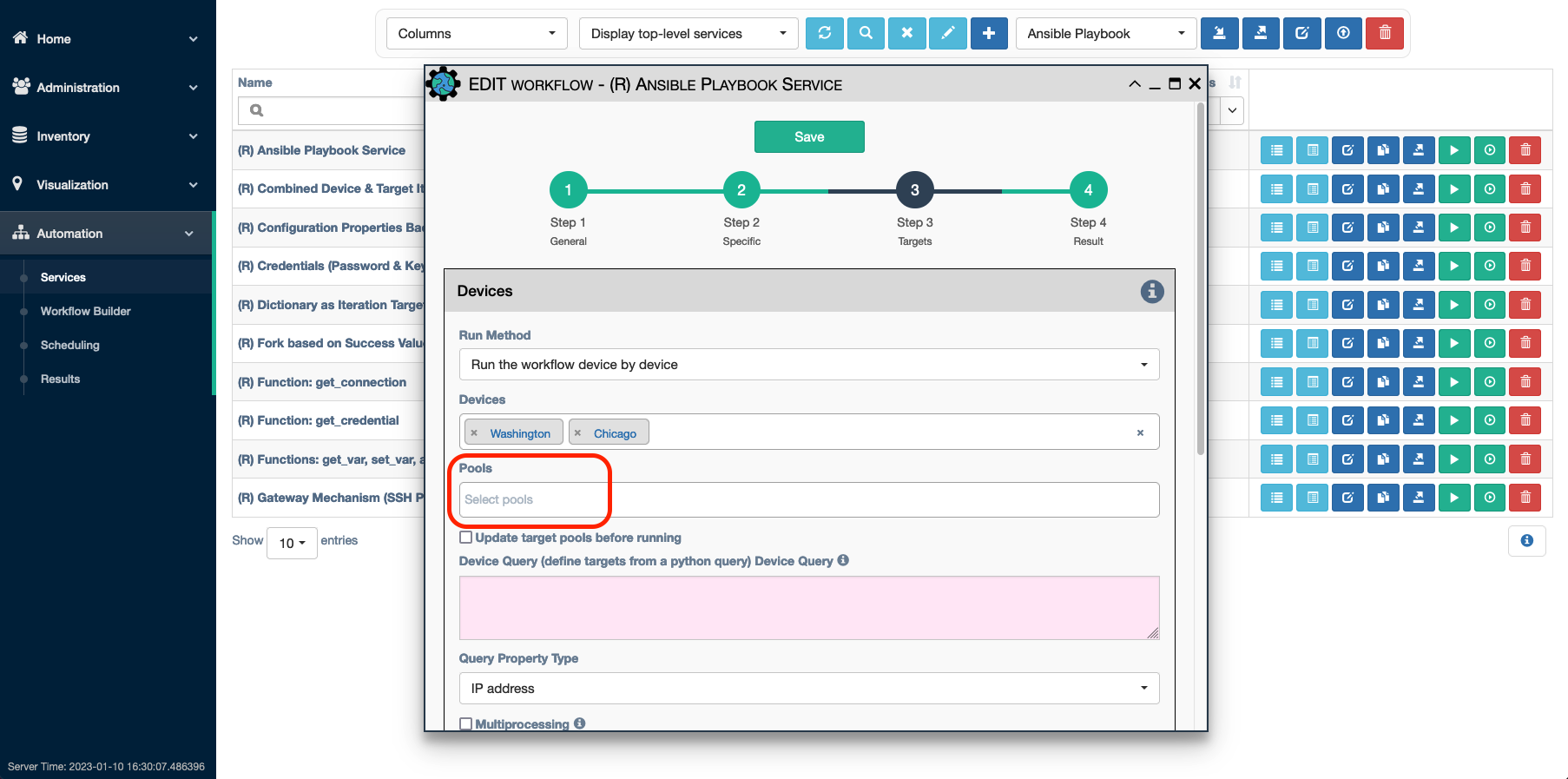
Pool Recalculation
All Pools are subject to automatic updates by eNMS (contingent upon the
fact that the Pool's Manually Defined flag is NOT set). Pool recalculations occur
in the following cases:
- When a new pool is created, it is (re)calculated.
- When the REST API migration_import and topology_import endpoints are run and their skip_pool_update parameter is not provided, and when update_all_pools endpoint is run
- After pulling or cloning the content from the git configuration
repository, and the applicable pool relies on
configurationand/oroperational dataparameter fields. - When a service runs that has
Update target pools before runningselected inStep 3of the service targets panel, only the target pools for that service are updated. - When a service runs that has
Update pools after runningselected inStep 1, all pools are updated once that service terminates.
To manually update a Pool:
- Click on the
Updatebutton of a desired pool in theInventory -> Pool Managementtable listing. - Click on the
Update all poolsbutton at the top of Pool Management panel.
Manual definition and Manually Defined option
Initially, by default, the devices and links within a pool are
determined automatically based on the pool properties. To disable automatic
recalculations for a Pool, first edit the pool and set Manually Defined to
enabled.
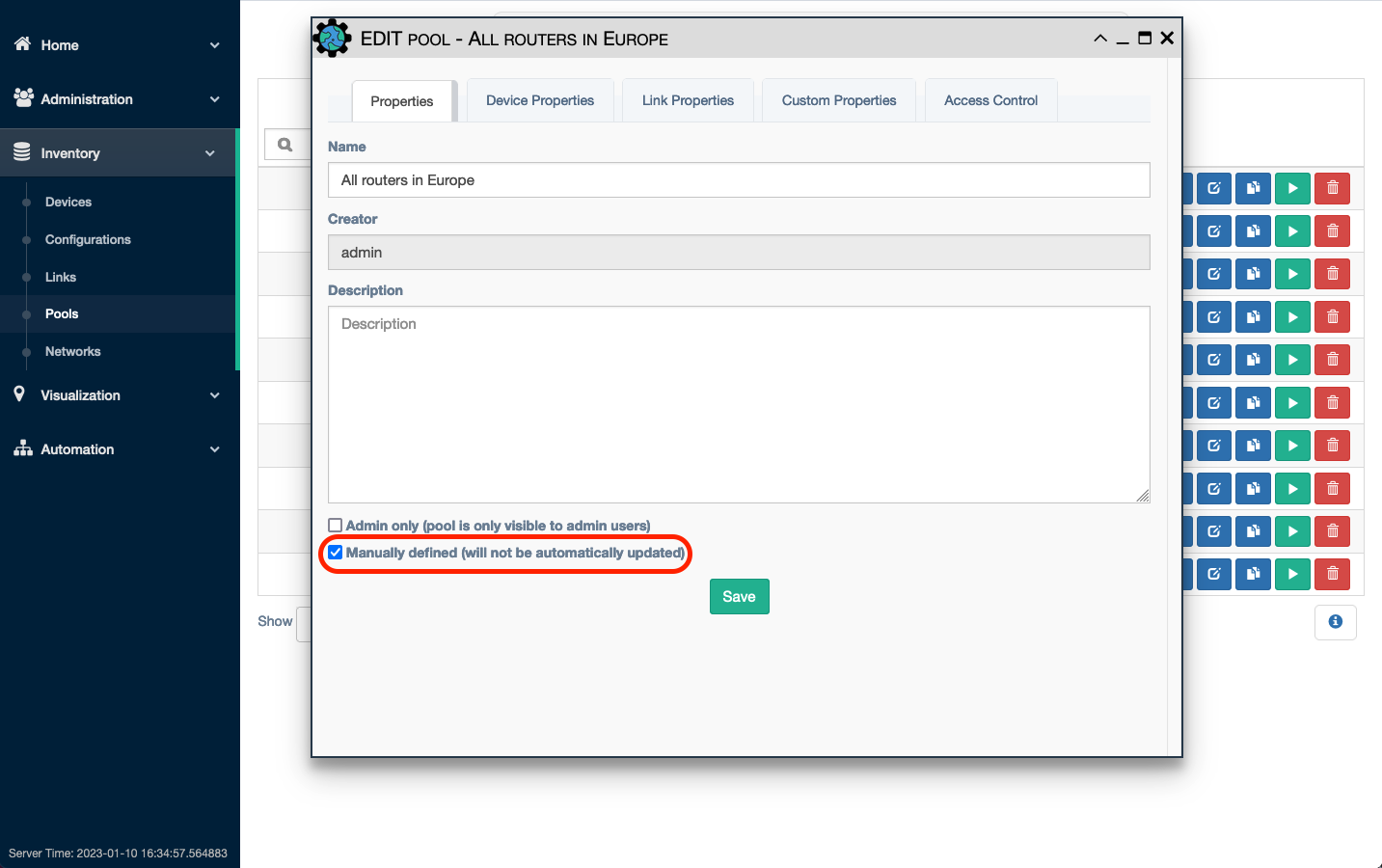
Next, the individual pools can be edited by the user clicking the hyperlink for
Devices or Links. The table for that object type's included members will be
displayed. Click the + button at the top of the table to add the object.
The user can select the devices to manually add from the inventory list or
paste a list of comma-separated devices from the clipboard (however, all devices
must exist in the inventory).
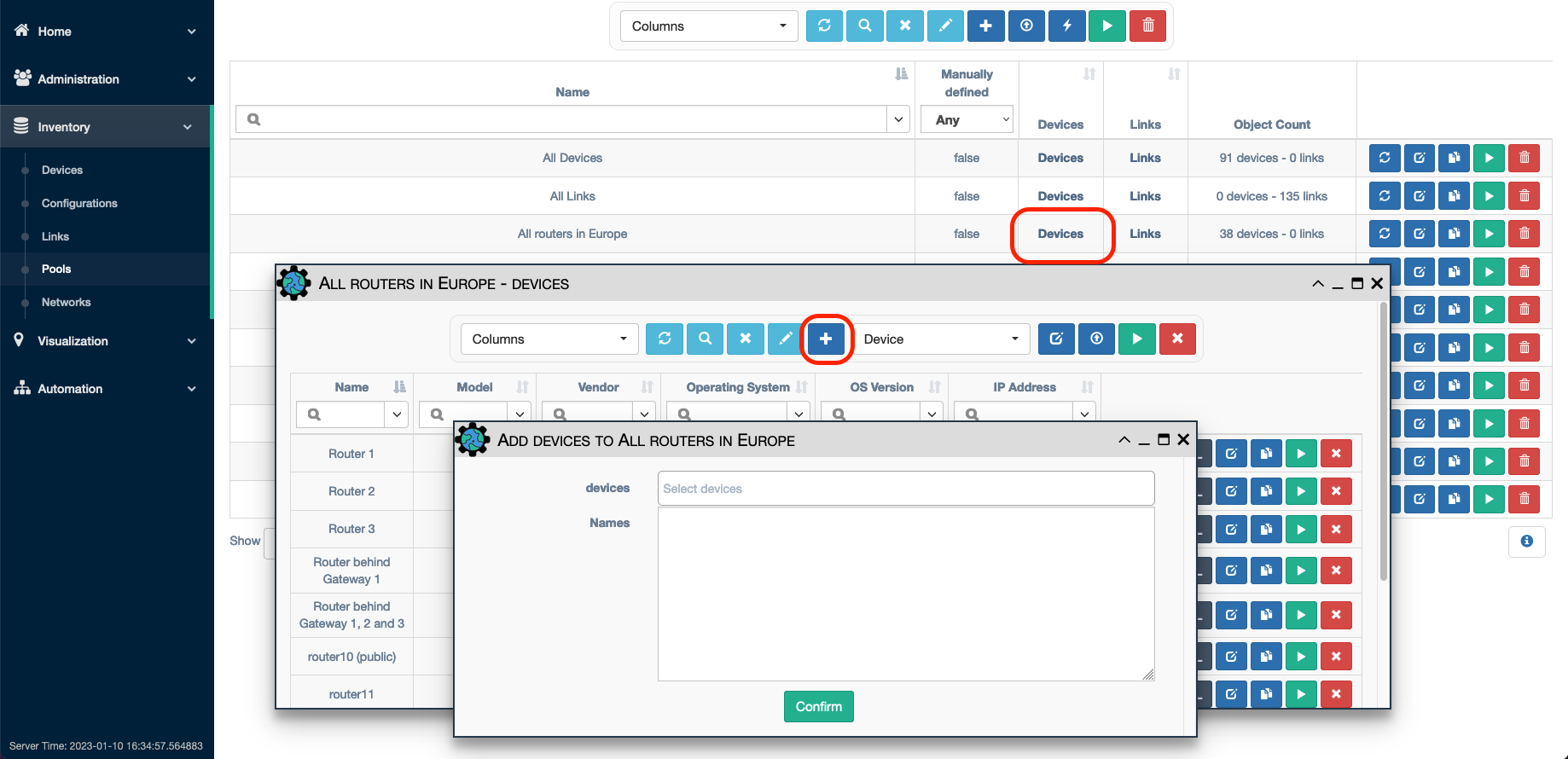
Note that pools with manually selected objects MUST have the Manually Defined
checkbox selected. This prevents manually selected pools from being recalculated
based on pool criteria. If the user wants to run against a pool that has some
criteria specified as well as some manually specified devices, it is advised to
have 2 pools: one with the criteria specified, and another with the manually
selected devices. When running a service, multiple pools and multiple devices can
be specified, and the service will run against all specified objects.
Note
Tip: the Bulk Delete button will clear a manually defined pool.